Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) revolutionized diesel engines by enhancing their efficiency and reliability, empowering commercial fleets to mitigate operational costs. But what's the backstory of EGR systems? How do they function, and what different types are there that you should be aware of to ensure your fleet runs with optimal cost-effectiveness.
In this article we’ll go through the following topics:
- What is an EGR Cooler?
- Why do we need EGR Coolers?
- How does EGR Cooler work?
- Detailed components of EGR Cooler
- Types of EGR Cooler
- Symptoms of a Bad EGR Cooler
What is an EGR Cooler?
An EGR cooler, short for "Exhaust Gas Recirculation" Cooler is a component in diesel internal combustion engines. It cools down exhaust gases and cuts down on releasing harmful NOx (nitrogen oxide) emissions before sending them back into the engine.
Why do we need an EGR Cooler?
It combines cooled exhaust gas with the air-fuel mixture inside the cylinder, decreasing the temperature during combustion. This process helps lower the engine's temperature and reduces harmful NOx (nitrogen oxide) emissions, making the engine eco-friendlier. This method is used to cut down on pollution, preventing overheating and potential damage to engine components.
.png)
How does EGR Cooler work?
Exhaust gases as it cools down travelling through the EGR Cooler. The EGR cooler mixes cooled exhaust gases with fresh air and fuel in the combustion chamber, lowering the combustion temperature to reduce harmful emissions like nitrogen oxides (NOx).
This process enhances engine efficiency by optimizing combustion, the table below step-by-step flowchart of how an EGR cooler system works:
|
The engine starts and runs, generating exhaust gases during combustion. |
|
When certain engine conditions are met (such as engine load and temperature), the EGR valve opens. |
|
The opened EGR valve allows a portion of the exhaust gases to flow out of the engine. |
|
Coolant from the engine's cooling system flows through the EGR cooler. |
|
The coolant absorbs heat from the recirculated exhaust gases as they pass through the EGR cooler. |
|
The exhaust gases, now cooled by the EGR cooler, mix with the incoming air-fuel mixture in the engine's combustion chamber. |
|
During the next combustion cycle, the cooled exhaust gases mix with the incoming air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. |
|
By lowering the combustion temperature, the EGR cooler helps reduce the formation of nitrogen oxides (NOx), which are harmful emissions. |
|
The recirculation of cooled exhaust gases can also improve engine efficiency and performance by optimizing combustion. |
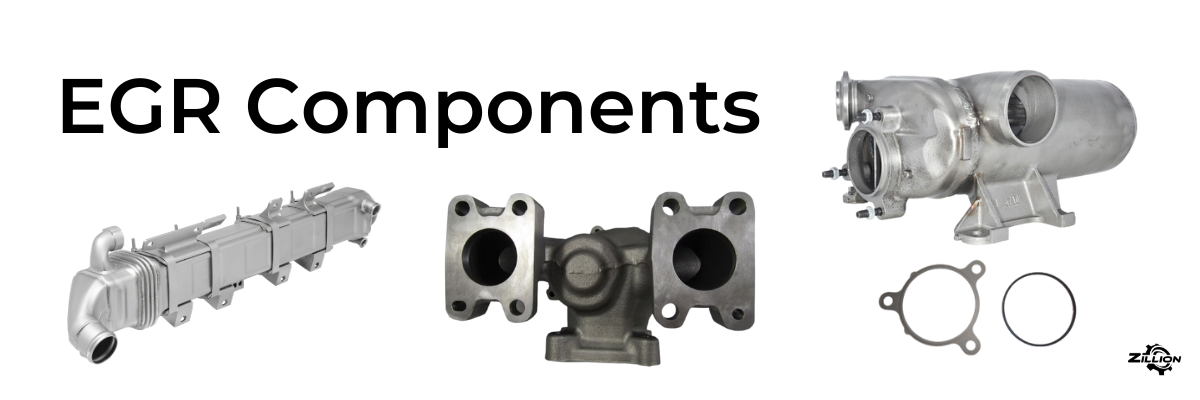
Detailed components of EGR Cooler:
- Intake Manifold: Hot exhaust gases enter here.
- Cooling Tubes: Gases flow through these tubes to cool down.
- Heat Exchange: Heat from the gases moves to the coolant.
- Coolant Circulation: Coolant absorbs the heat.
- Outtake Manifold: Cooled gases exit here.
- EGR Valve: Send the right amount of gas to enter the combustion chambers.
- Housing: Everything is enclosed and protected.
- Gaskets and Seals: These make sure everything stays sealed tight, no leaks.
The Main Components of EGR Cooler Systems:
1. EGR Valves: These valves control the flow of exhaust gases into the intake manifold. They regulate the amount of recirculated exhaust gas based on engine operating conditions and emission requirements.
2. EGR Coolers: EGR coolers handle reducing the temperature of the recirculated exhaust gases before they are reintroduced into the engine's combustion chamber. By cooling the exhaust gases, EGR coolers help prevent engine knocking, reduce NOx emissions, and improve engine efficiency.
Types of Diesel EGR Systems Based on Temperature:
1. Low-Temperature EGR (LT-EGR): Recirculates cooler exhaust gases back to engine.
2. High-Temperature EGR (HT-EGR): Recirculates hotter exhaust gases back to engine.
While these terms describe different strategies for recirculating exhaust gases based on temperature, both LT-EGR and HT-EGR systems can utilize various types of EGR coolers, depending on engine requirements and emissions regulations.

Conclusion
Understanding EGR Cooler’s role, functionality, and importance becomes essential for both automotive enthusiasts and industry professionals, as they continue to be a part in achieving environmental sustainability and advancing automotive engineering.
Zillion Heavy Duty Parts believes in cultivating leadership that will reshape the future. Sharing knowledge is a journey to redefining the industry. Visit ZillionHD.com for more information on how to become a Zillion distributor. Join us in revolutionizing the trucking industry and creating a future where liberty knows no bounds. To learn more about heavy duty parts listen to The Heavy Duty Parts Report





